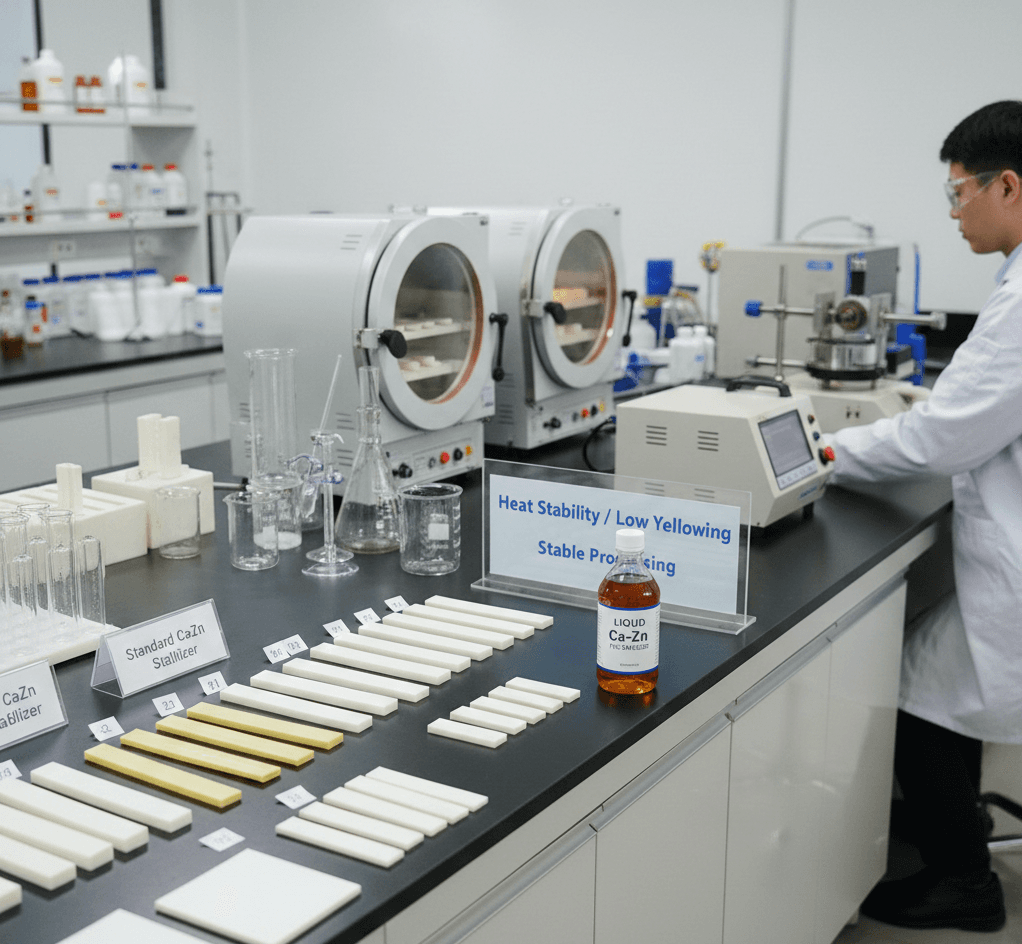
1.The synergistic effect of metal soaps
According to the active mechanism of metal soaps in preventing the degradation of PVC, metal soaps can be classified into two categories: one can only absorb HCL and prevent its catalytic effect on the HCL removal reaction. The most representative examples are barium soaps and calcium soaps. The thermal stability of this type of metal is average. Its initial stability is not good, but when exposed to heat for a long time, the stability of PVC does not change much. The metal chlorides generated during its stabilization process have basically no catalytic effect on the removal of HCL. Another type not only absorbs HCL but also reacts with allyl chloride to stabilize PVC. The most representative examples are zinc soaps and cadmium soaps. This type of metal soap has good initial coloring properties, but when exposed to heat for a long time, the products will change color sharply. Especially zinc soap, it is extremely prone to rapid oxidation, resulting in what is called the "zinc burning" phenomenon. This is because the chlorides CdCl2 and ZnCl2 generated during the stabilization process of zinc soap and cadmium soap are extremely strong lewis acids and act as catalysts for the HCL removal reaction. Based on the above characteristics, it is very difficult to achieve satisfactory results by using any type of metal soap alone. If highly active cadmium and zinc soaps are used in combination with less active barium and calcium, both the initial coloring property and long-term stability can be improved. For instance, when barium is used in combination with cadmium soap, the cadmium soap first undergoes esterification with allyl chloride in PVC molecules, generating CdCl2 which then undergoes a double decomposition reaction with the barium soap, regenerating cadmium and rendering CdCl2 harmless. The same principle applies to calcium and zinc soaps, as well as barium and zinc soaps.
2. The synergistic effect of phosphites and metal soaps
When phosphite esters are used in combination with metal soaps, they can react with metal chlorides to inhibit their catalytic effect on the removal of HCL, thereby enhancing the thermal stability efficiency of the system.
3. The synergistic effect of most alcohols and metal soaps
The combination of many alcohols and metal soaps can significantly prolong the permeability period of HCL removal and can also inhibit the discoloration of the resin. It is generally believed that polyols exert a synergistic effect by complexing with metal chlorides and inhibiting their catalytic effect on the removal of HCL.
4. The synergistic effect of β -diketone compounds and metal soaps
β -diketone compounds can react with PVC through carboalkyl interaction, thereby stabilizing it, but the reaction rate is slow. If used in combination with systems such as calcium/zinc, the speed of the stabilization reaction can be greatly increased. The ionization potential energy of metallic zinc soap is relatively high. It reacts with allyl chlorine to esterify and stabilize PVC. As a by-product, ZnCl2 serves as a catalyst for the removal of HCL, and its presence is harmful. However, ZnCl2 is also a catalyst for carboalkylation. The addition of β -diketone compounds precisely takes advantage of this catalytic effect of ZnCl2, enabling the carboalkylation reaction of allyl chloride to proceed rapidly. The synergistic effect of β -diketone compounds with barium/zinc is similar to this.
5. Synergistic effect of rare earth stabilizers and zinc soaps
Rare earth stabilizers themselves have the effect of displacing allyl chlorine, but when used alone, PVC products show yellow discoloration. When used in combination with zinc soap, the exchange reaction between ZnCl2 produced during the stabilization process of zinc soap and rare earth ions generates ReCl3, which is less harmful. In addition, rare earths preferentially react with HCL to form rare earth chlorinated hydroxy acids, which reduces the catalytic effect of ZnCl2 on the removal of HCL. The combination of the two components has achieved better initial coloring and significantly enhanced long-term stability.