PET/EVOH/PE High-Barrier Thermoforming Sheet Rolls
What EVOH Is, Common Structure Combinations, Key Applications (MAP/Pharma/Cosmetics) + Copy-Ready Specs
This guide focuses on PET/EVOH/PE high-barrier thermoforming sheet rolls for MAP trays, covering EVOH basics, common structures, and practical RFQ specs.
If you’re searching for high-barrier thermoforming sheet, you’ll likely see queries like:
“EVOH barrier sheet” “PET/EVOH/PE sheet roll” “MAP meat tray material”.
This article is written in a product-page + blog style to help buyers and engineers spec the right material faster:
-
What EVOH is (and a key limitation you must know)
-
Common EVOH multilayer structure combinations
-
Where PET/EVOH/PE is commonly used (supermarket MAP foods, pharma, cosmetics)
-
How to write OTR/WVTR specs correctly (test conditions + flat vs formed)
-
Seal window + microleaks (seal integrity first, then barrier)
-
A copy-paste RFQ checklist to reduce trial loops
1) What is EVOH?
EVOH (ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer) is one of the most widely used high-barrier core materials in packaging—especially known for excellent oxygen/gas barrier performance.
Key note (important for accurate specs)
-
EVOH’s barrier performance is humidity-sensitive. In higher humidity, EVOH’s gas barrier can drop significantly.
That’s why EVOH is typically used as a middle barrier layer, protected between outer layers (e.g., PET/PP/PE) in a multilayer structure.
Buyer takeaway: Always define test conditions (temperature + %RH) when you request OTR/WVTR for EVOH structures.
In short, PET/EVOH/PE high-barrier thermoforming sheet rolls use EVOH as a protected barrier core to support MAP shelf-life targets.
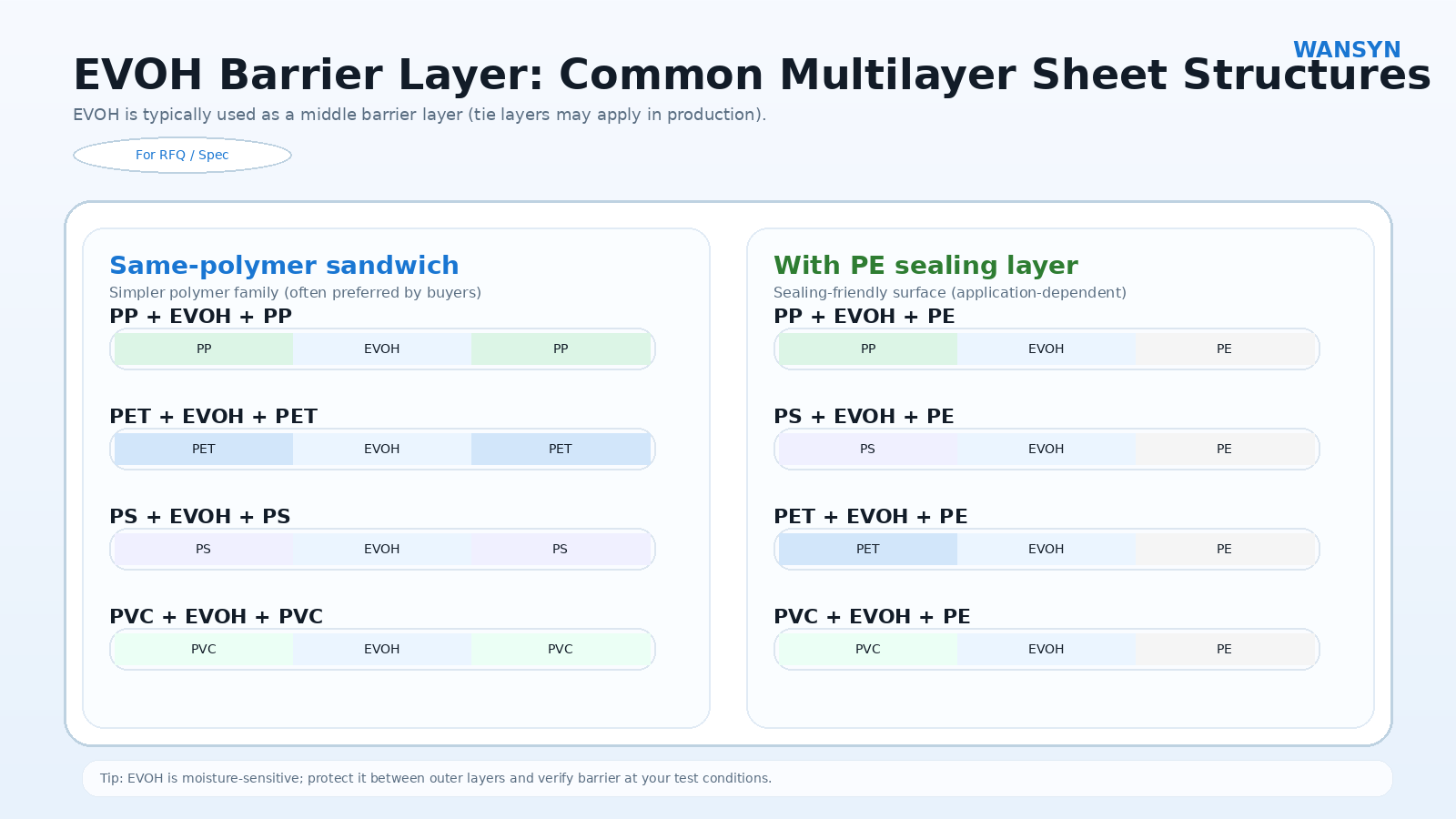
2) Common EVOH multilayer structures (copy into RFQs)
EVOH is usually a middle barrier layer in thermoforming sheets. Common combinations include:
Same-polymer sandwich structures
-
PP + EVOH + PP
-
PET + EVOH + PET
-
PS + EVOH + PS
-
PVC + EVOH + PVC
EVOH with PE sealing layer (sealing-friendly surface)
-
PP + EVOH + PE
-
PS + EVOH + PE
-
PET + EVOH + PE (this article’s focus: PET/EVOH/PE)
-
PVC + EVOH + PE
Note: tie layers may be used in production, but most buyers can specify the core structure + performance targets.
3) Why choose PET/EVOH/PE for high-barrier trays?
PET/EVOH/PE works well for many supermarket programs because each layer plays a clear role:
-
PET: clarity, stiffness, forming stability (premium display)
-
EVOH: high oxygen/gas barrier core (shelf-life support)
-
PE: sealing-friendly surface + moisture-resistant outer layer (helps protect the EVOH core)
This structure is often selected for MAP projects where barrier and sealing must work together—not just “high barrier on paper”.
4) Typical applications
4.1 Supermarket MAP food packaging (core market)
-
MAP meat & poultry trays (color stability + shelf life)
-
MAP seafood trays (oxidation-sensitive products)
-
Ready meals / deli foods / prepared foods (longer chilled display needs)
4.2 Pharmaceutical packaging (market-dependent)
Some pharma/medical-related packaging requires high barrier to protect sensitive products (final suitability depends on local regulations and compliance requirements).
4.3 Cosmetics & personal care packaging
Many cosmetic and personal-care products are oxygen/volatile-sensitive and benefit from high-barrier packaging structures to help preserve performance and shelf life.
5) How to specify OTR/WVTR so suppliers can quote correctly
Most RFQs fail because they only say “high barrier” without specifying test conditions and test basis.
OTR/WVTR spec must include:
-
Target OTR and WVTR values
-
Test conditions (temperature + %RH)
-
Test basis: flat sheet or formed tray?
Why “formed tray” matters: thermoforming can thin corners (deep draw zones), which can change effective barrier and sealing performance at the weakest points.

6) MAP reality: Microleaks beat barrier (seal integrity first)
Here’s a practical truth for MAP programs:
Seal integrity comes first. Microleaks can defeat a high-barrier EVOH structure.
Common microleak sources:
-
wrinkles → channel leaks
-
contamination (juice/oil/powder) on the flange
-
uneven pressure / worn pads / seal head flatness
-
Read the full MAP guide on OTR/WVTR + microleaks:
MAP Meat/Seafood Trays: OTR/WVTR + Seal Integrity (Microleak) -
If your line shows leaks/wrinkles/stringing, use this troubleshooting checklist:
Tray Sealing Troubleshooting: Easy-Peel Failures, Wrinkles, Leaks & Stringing

7) Where PET/EVOH/PE fits vs other laminates (quick selection logic)
-
PET/EVOH/PE: when barrier (especially oxygen barrier) is a priority for MAP shelf life, while keeping sealing-friendly surface requirements.
-
PET/PE: sealing-friendly baseline when barrier targets are not extreme.
-
PET/CPP: premium clarity + sealing stability + print durability options.
-
PP/CPP: toughness and cold-chain handling focus (e.g., -20°C programs).
For a complete supermarket tray selection framework (barrier + anti-fog + easy-peel + printing), see:
Supermarket Meat/Seafood/Sushi Trays: Laminated Sheets (Barrier + Anti-fog + Easy-peel + Print)
8) Product-style specification (example ranges; customize per project)
-
Structure: PET/EVOH/PE (custom EVOH multilayer structures available)
-
Process route: lamination or multilayer co-extrusion
-
Form: roll or sheet
-
Thickness : 0.15–2.0 mm (depends on tray depth/draw ratio)
-
Width : 170–1350 mm (depends on thermoforming line and tooling)
-
Surface: gloss / matte / anti-fog
-
Optional functions: easy-peel compatibility (depends on lidding system), printing grades, barrier targets (OTR/WVTR)
9) Copy-paste RFQ checklist
Use this RFQ template to source PET/EVOH/PE high-barrier thermoforming sheet rolls with clear test conditions and sealing requirements.
Application: MAP meat / seafood / deli / prepared foods / pharma / cosmetics
Shelf-life target: ____ days; storage: 0–4°C / -18°C
Tray design: depth ____ mm; flange width ____ mm; corner radius ____ mm
Structure: PET/EVOH/PE or (PP/PS/PET/PVC)+EVOH combinations
Form: roll / sheet; thickness ____ mm; width ____ mm; OD ____; core ____
OTR target: ____ (test: ___°C / ___%RH)
WVTR target: ____ (test: ___°C / ___%RH)
Test basis: flat sheet / formed tray
Sealing equipment: ____ ; temp ____°C; pressure ____ ; dwell ____ s
Seal integrity: no microleaks/channel leaks; easy-peel required? yes/no
Finish: gloss / matte / anti-fog; printing yes/no
Compliance market: EU / US / SEA / other: ____
FAQ
Q1: What is EVOH used for in packaging?
EVOH is a high-barrier core layer used mainly to improve oxygen/gas barrier performance in multilayer packaging structures.
Q2: Why does humidity matter for EVOH?
EVOH barrier performance is humidity-sensitive, so test conditions (especially %RH) must be specified, and EVOH is typically protected between outer layers.
Q3: Why does MAP shelf life fail even with “high barrier” material?
Microleaks and unstable sealing often defeat barrier performance first. Verify seal integrity and seal window, then optimize OTR/WVTR.